Combinational Logic - Adders
📌 Introduction
In digital logic design, adders are fundamental building blocks used for performing binary addition.
A half adder adds two single-bit inputs, while a full adder also includes a carry-in input.
By cascading full adders, we can construct a ripple-carry adder to handle multi-bit operations.
Categories
🧑💻 Code Example
Half Adder
module top_module(
input a, b,
output cout, sum );
assign cout = a & b;
assign sum = a ^ b;
endmodule
Full Adder
module top_module(
input a, b, cin,
output cout, sum );
assign cout = (a & b) | (a & cin) | (b & cin);
assign sum = a ^ b ^ cin;
endmodule
3-bit Binary Ripple-Carry Adder
module Fadd(
input a, b, cin,
output cout, sum );
assign cout = (a & b) | (a & cin) | (b & cin);
assign sum = a ^ b ^ cin;
endmodule
module top_module(
input [2:0] a, b,
input cin,
output [2:0] cout,
output [2:0] sum );
Fadd Add0(.a(a[0]), .b(b[0]), .cin(cin), .cout(cout[0]), .sum(sum[0]));
Fadd Add1(.a(a[1]), .b(b[1]), .cin(cout[0]), .cout(cout[1]), .sum(sum[1]));
Fadd Add2(.a(a[2]), .b(b[2]), .cin(cout[1]), .cout(cout[2]), .sum(sum[2]));
endmodule
4-bit Binary Ripple-Carry Adder
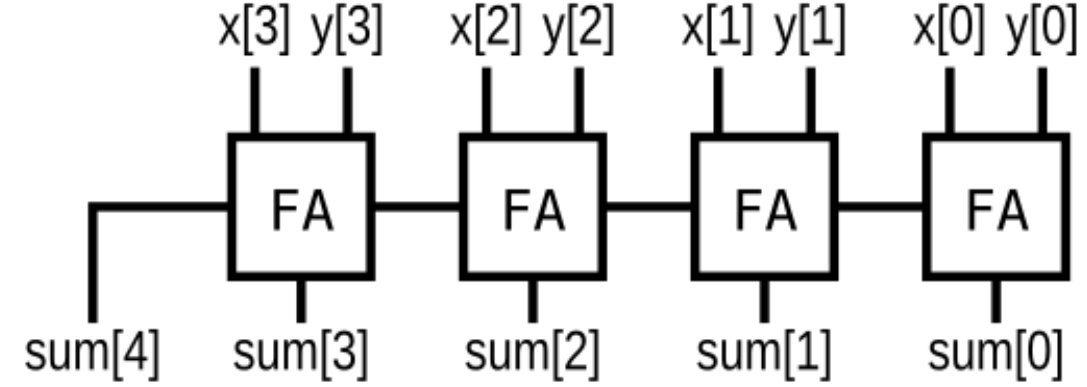
module FA(input a, input b, input cin, output sum, output cout);
assign sum = a ^ b ^ cin;
assign cout = (a & b) | (a & cin) | (b & cin);
endmodule
module top_module (
input [3:0] x,
input [3:0] y,
output [4:0] sum);
wire [2:0] cout;
FA add0(.a(x[0]), .b(y[0]), .cin(1'b0), .sum(sum[0]), .cout(cout[0]));
FA add1(.a(x[1]), .b(y[1]), .cin(cout[0]), .sum(sum[1]), .cout(cout[1]));
FA add2(.a(x[2]), .b(y[2]), .cin(cout[1]), .sum(sum[2]), .cout(cout[2]));
FA add3(.a(x[3]), .b(y[3]), .cin(cout[2]), .sum(sum[3]), .cout(sum[4]));
endmodule
Signed Addition Overflow (Two’s Complement)
Definition: Overflow occurs when the carry into the MSB differs from the carry out of the MSB, or equivalently when adding two numbers with the same sign produces a result with the opposite sign.
My Answer
module top_module (
input [7:0] a,
input [7:0] b,
output [7:0] s,
output overflow
); //
assign s = a + b;
assign overflow = ((a[7]==1'b0 & b[7]==1'b0 & s[7]==1'b1)
| (a[7]==1'b1 & b[7]==1'b1 & s[7]==1'b0));
endmodule
Best Answer
module top_module (
input [7:0] a,
input [7:0] b,
output [7:0] s,
output overflow
);
wire [8:0] sum_extended = {1'b0, a} + {1'b0, b};
assign s = sum_extended[7:0];
// Cin_7 = Sum_7 ^ a[7] ^ b[7]
assign overflow = sum_extended[8] ^ sum_extended[7] ^ a[7] ^ b[7];
endmodule
If the carry into bit 7 and the carry out of bit 7 are different, overflow occurs.
100-bit Binary Adder
module top_module(
input [99:0] a, b,
input cin,
output cout,
output [99:0] sum );
assign {cout, sum} = {1'b0, a} + {1'b0, b} + {100'b0, cin};
endmodule
behavioral code
4-bit BCD adder (ripple-carry)
My Answer
module bcd(input [3:0] a, b,
input cin,
output reg cout,
output reg [3:0] sum);
wire [4:0] temp_sum = {1'b0, a} + {1'b0, b} + {4'b0, cin};
always @(*) begin
cout = 1'b0;
sum = 4'b0;
if (temp_sum>=5'd10) begin
{cout, sum} = temp_sum - 5'd10;
cout = 1'b1;
end
else begin
{cout, sum} = temp_sum;
end
end
endmodule
module top_module (
input [15:0] a, b,
input cin,
output cout,
output [15:0] sum );
genvar i;
wire [4:0] c;
assign c[0] = cin;
generate
for (i=0; i<4; i++) begin:Bcdadd4
bcd add(.a(a[4*i+3:4*i]), .b(b[4*i+3:4*i]), .cin(c[i]),
.cout(c[i+1]), .sum(sum[4*i+3:4*i]));
end
endgenerate
assign cout = c[4];
endmodule
+6 Answer
module bcd(input [3:0] a, b,
input cin,
output reg cout,
output reg [3:0] sum);
wire [4:0] temp_sum = {1'b0, a} + {1'b0, b} + {4'b0, cin};
always @(*) begin
cout = 1'b0;
sum = temp_sum[3:0];
if (temp_sum>9) begin
{cout, sum} = temp_sum + 5'd6; // force hex carry, 10->16
end
end
endmodule
module bcd(input [3:0] a, b,
input cin,
output cout,
output [3:0] sum);
wire [4:0] temp_sum = {1'b0, a} + {1'b0, b} + {4'b0, cin};
assign {cout, sum} = (temp_sum>9) ? temp_sum + 5'd6 : temp_sum;
endmodule
- The BCD representation for the 5-digit decimal number 12345 is 20’h12345. This is not the same as 14’d12345 (which is 14’h3039).
- The circuit is structured just like a binary ripple-carry adder, except the adders are base-10 rather than base-2.