5-bit LFSR (HDLBits)
Galois Linear Feedback Shift Register
📌 Question
A linear feedback shift register is a shift register usually with a few XOR gates to produce the next state of the shift register. A Galois LFSR is one particular arrangement where bit positions with a “tap” are XORed with the output bit to produce its next value, while bit positions without a tap shift. If the taps positions are carefully chosen, the LFSR can be made to be “maximum-length”. A maximum-length LFSR of n bits cycles through 2n-1 states before repeating (the all-zero state is never reached).
The following diagram shows a 5-bit maximal-length Galois LFSR with taps at bit positions 5 and 3. (Tap positions are usually numbered starting from 1). Note that I drew the XOR gate at position 5 for consistency, but one of the XOR gate inputs is 0.
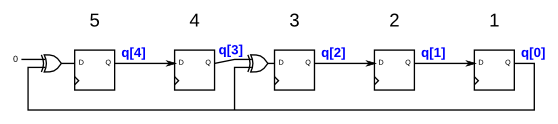
Hint
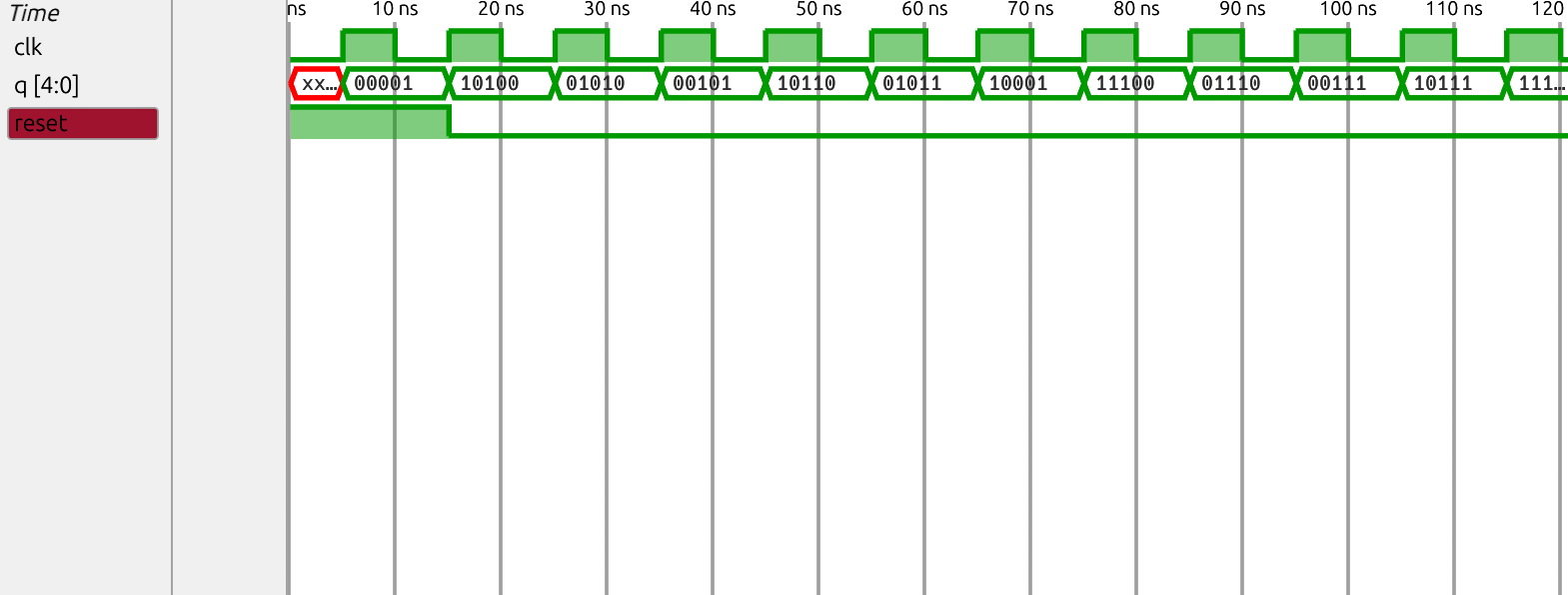
The first few states starting at 1 are 00001, 10100, 01010, 00101, ... The LFSR should cycle through 31 states before returning to 00001.
🧑💻 Code Example
RTL
module top_module(
input wire clk,
input wire reset, // Active-high synchronous reset to 5'h1
output reg [4:0] q
);
always@(posedge clk) begin
if (reset)
q <= 5'h1;
else
q <= { (q[0]^1'b0), q[4], (q[3]^q[0]), q[2:1] };
end
endmodule
Testbench
`timescale 1ns/1ps
module tb_top_module;
reg clk;
reg reset;
wire [4:0] q;
top_module dut (
.clk(clk),
.reset(reset),
.q(q)
);
initial clk = 0;
always #5 clk = ~clk;
initial begin
reset = 1;
#15;
reset = 0;
#400;
reset = 1;
#20;
reset = 0;
#50;
$display("Simulation Finished");
$finish;
end
initial begin
$display("Time\t Reset\t q (Hex)\t q (Bin)");
$monitor("%t\t %b\t %h\t\t %b", $time, reset, q, q);
end
initial begin
$dumpfile("tb_top_module.vcd");
$dumpvars(0, tb_top_module);
end
endmodule
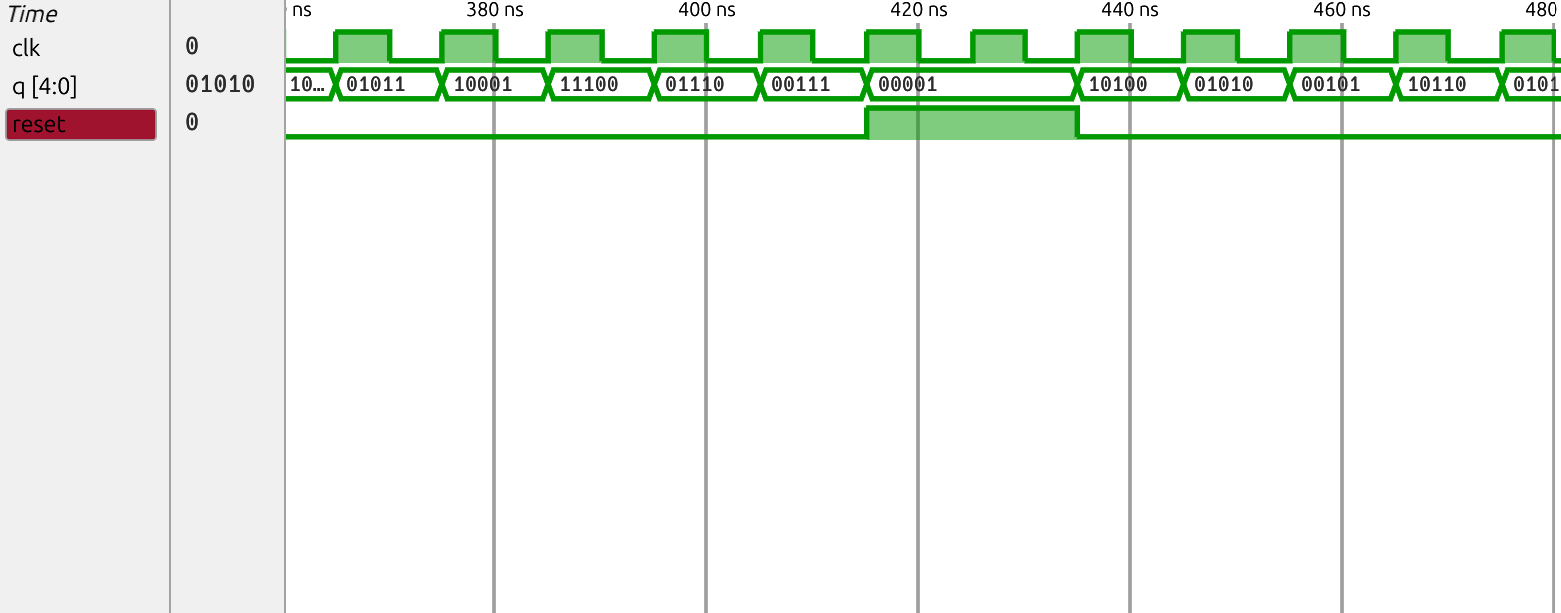
Waveform
RTL Schematic
Gate-level Schematic
🔬 Results