D Flip-Flop with Reset
📌 Introduction
This note compares two common D flip-flop designs — one with an asynchronous reset and one with a synchronous reset.
-
Asynchronous reset: The output
qis immediately cleared to0when the reset signal is asserted, regardless of the clock.
This is often used for global power-on reset circuits. -
Synchronous reset: The reset only takes effect on the clock’s rising edge.
It avoids metastability issues during reset release and is more suitable for synthesis and timing control.
| Type | Sensitivity List | Reset Timing | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asynchronous Reset | @(posedge clk or posedge ar) |
Immediate | Power-on reset, quick fault recovery |
| Synchronous Reset | @(posedge clk) |
On next clock edge | Regular sequential logic, easier STA |
🧑💻 Code Example
Asynchronous Reset DFF
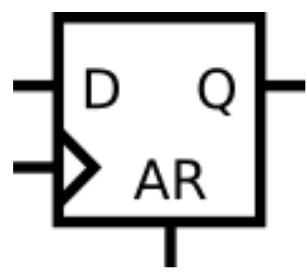
module top_module (
input clk,
input d,
input ar, // asynchronous reset
output q);
always @(posedge clk, posedge ar) begin
if (ar)
q<=1'b0;
else
q<=d;
end
endmodule
Synchronous Reset DFF
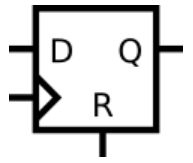
module top_module (
input clk,
input d,
input r, // synchronous reset
output q);
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (r)
q<=1'b0;
else
q<=d;
end
endmodule